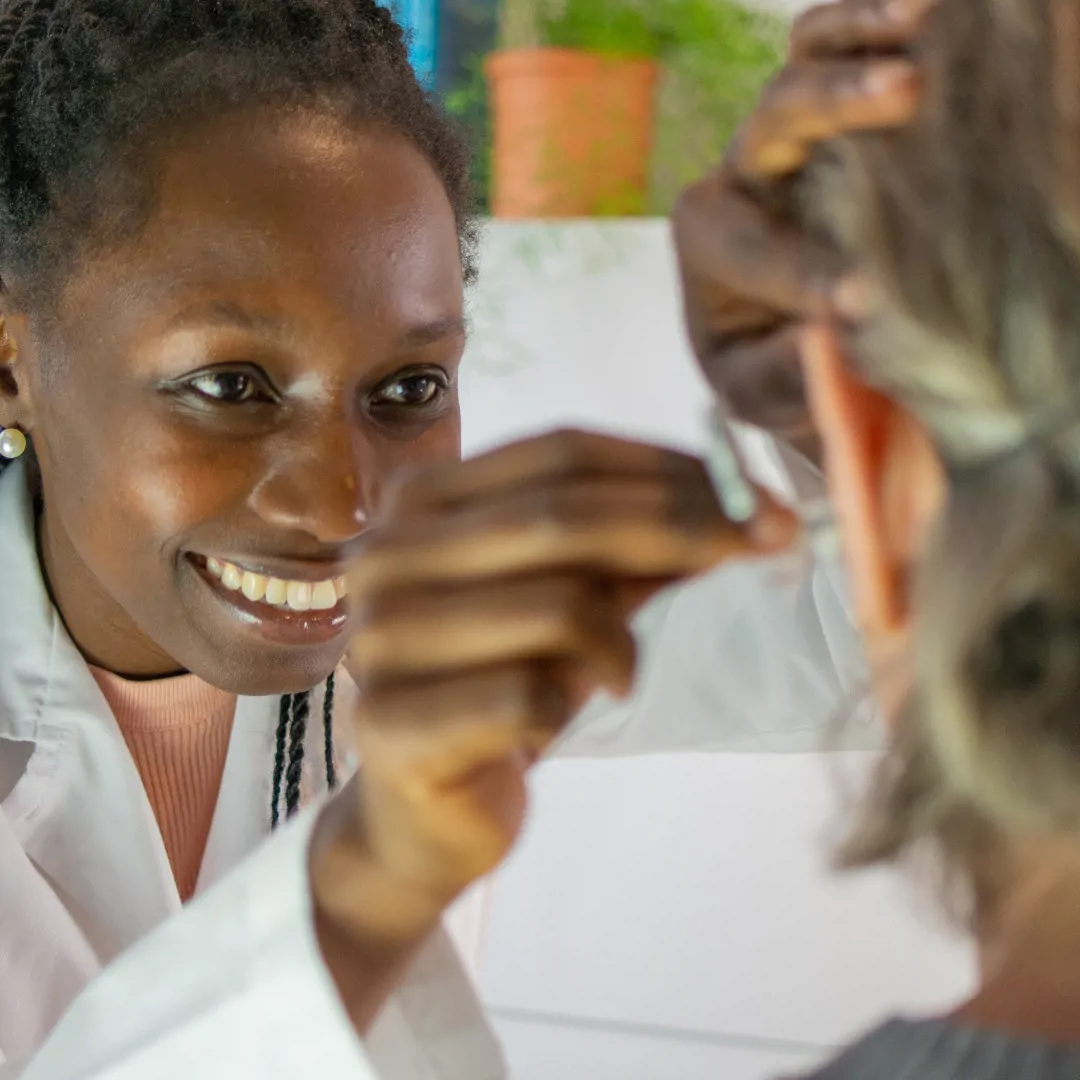
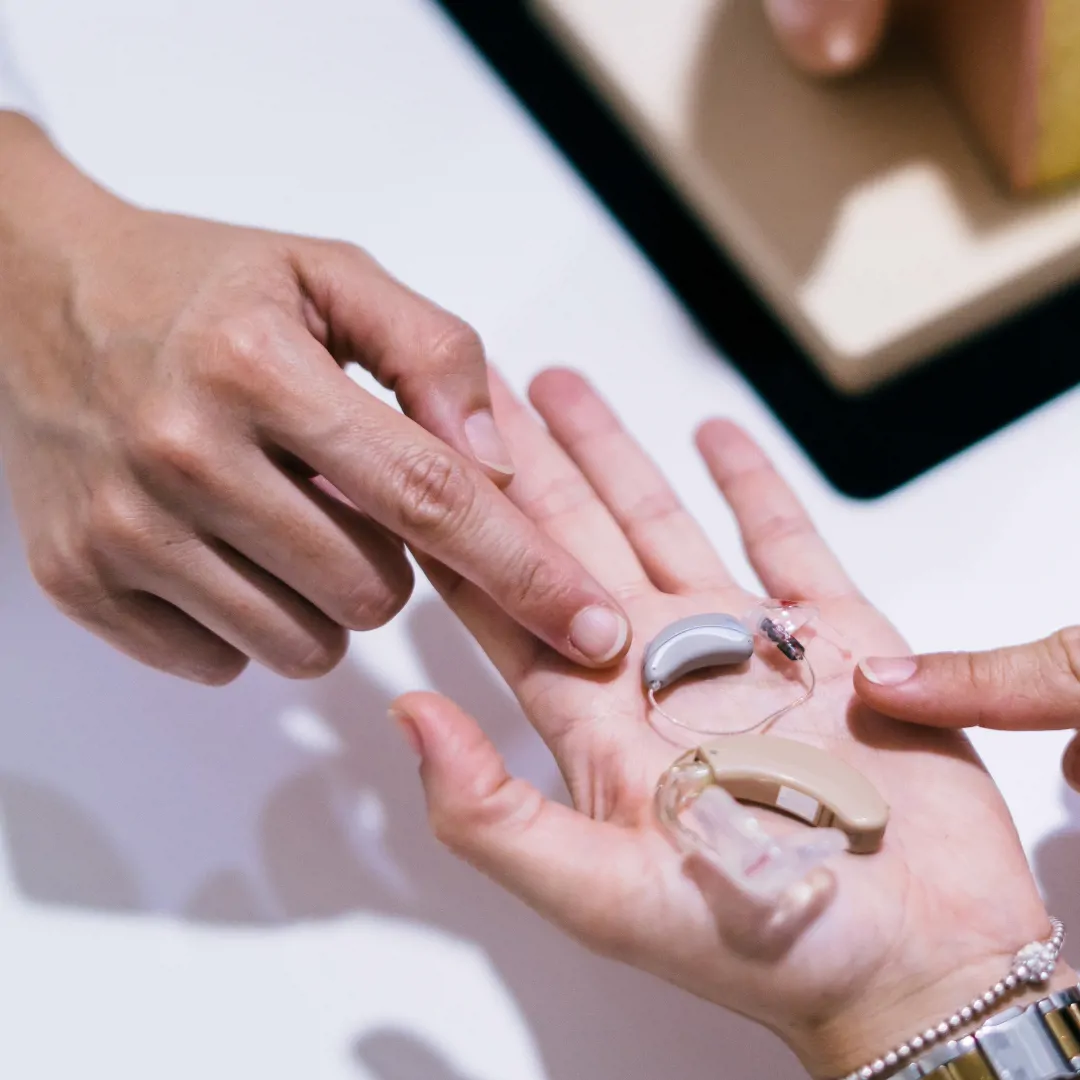
Entry into Audiology


How to Become an Audiologist
Seeking a career in Audiology? Look no further. Quad Recruitment have a comprehensive guide on how to become an audiologist.
To view your future opportunities click the link below
1. Educational Requirements
A-Level Studies (or Equivalent)
- Subjects: Typically, you will need A-levels (or equivalent) in subjects such as Biology, Physics, Chemistry, or Mathematics.
- Grades: High grades are essential, often BBB or above.
Bachelor’s Degree: BSc (Hons) in Audiology
- Course Duration: 3-4 years.
- Accredited Universities: Ensure the audiology degree is from a university accredited by the Health and Care Professions Council (HCPC) and/or the Registration Council for Clinical Physiologists (RCCP).
- Content: The course covers topics including auditory and vestibular systems, hearing assessment, hearing aids, cochlear implants, tinnitus, balance disorders, and patient care.

2. Clinical Training
Placements During Degree
- Integrated Placements: Clinical placements are typically integrated into the audiology degree program, allowing students to gain hands-on experience in various settings such as hospitals, clinics, and private practices.
- Activities: Applying theoretical knowledge, developing practical skills, and gaining experience under the supervision of qualified audiologists.

3. Professional Registration
HCPC Registration
- Requirements: Successful completion of an accredited BSc Audiology degree.
- Application Process: Submit an application to the HCPC with the necessary documentation and fees.
- HCPC Registration: Once registered, you are legally allowed to practice as an audiologist in the UK.

4. Continuous Professional Development (CPD)
Ongoing Learning
- Mandatory CPD: Audiologists must engage in CPD to maintain their registration and ensure their skills and knowledge are up-to-date.
- Types of CPD: Includes attending courses, workshops, seminars, and self-directed study.

5. Career Specialisation and Further Training
Options for Specialisation
- Adult Audiology: Working with adults with hearing and balance disorders.
- Pediatric Audiology: Specializing in hearing and balance disorders in children.
- Educational Audiology: Working within educational settings to support children with hearing impairments.
- Clinical Research: Involvement in research to advance the field of audiology.
- Hearing Therapy: Specializing in counseling and rehabilitative support for individuals with hearing loss.
Further Qualifications
- Postgraduate Degrees: Opportunities for further study include MSc in Audiology, PhD, or other specialist qualifications.
- Professional Certifications: Additional certifications in areas such as vestibular assessment, tinnitus management, or auditory processing disorders.

6. Additional Considerations
Overseas Audiologists
- Adaptation Programmes: Overseas-trained audiologists may need to complete adaptation programs and additional assessments to meet HCPC requirements.
Work Experience
- Summer Placements: Engaging in internships or placements during the BSc course can provide valuable experience and improve employability.
Professional Memberships
- Professional Bodies: Joining organizations like the British Academy of Audiology (BAA) or the British Society of Audiology (BSA) can provide access to resources, networking opportunities, and professional support.

Already a Qualified Audiologist?
We'd love to speak with you about our active roles! We have many opportunties for you to explore and discuss with a consultant. Drop off your CV with us to discuss your future.